FreeBSD: How To Install FreeBSD 8.x from USB Flash Drive
FreeBSD 8 can be installed from a USB memory stick. The required files can be downloaded via FTP:
i386: ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD/releases/amd64/ISO-IMAGES/8.2/FreeBSD-8.2-RELEASE-amd64-memstick.img
amd64: ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD/releases/amd64/ISO-IMAGES/8.2/FreeBSD-8.2-RELEASE-amd64-memstick.img
Insert the USB drive into the computer running Linux/FreeBSD and make sure it gets detect by the Kernel. You can check if the USB device got detect or not by running the following command:
dmesg
 Print This Post
Print This Post
Linux: How To Create a USB Debian Installation Flash Drive
In this tutorial I'll show you how to create a USB drive which can be used as an installation media to install Debian Linux.
You will need a computer which is already running Linux and a USB flash drive of size at least 256 MB which we will prepare as our installation media.
Insert the USB drive into the computer running Linux and make sure it gets detect by the Linux Kernel. You can check if the USB device got detect or not by running the following command:
dmesg
and you should see something like this:
[143981.321725] sd 8:0:0:0: [sdb] .321725 512-byte hardware sectors (1024 MB)
[143981.522718] sd 8:0:0:0: [sdb] Write Protect is off
....
[143981.522719] sd 8:0:0:0: [sdb] Attached SCSI disk
 Print This Post
Print This Post
How To Set Up an OpenBSD Router – Step-by-Step Tutorial
This article is a step-by-step guide about how to set up OpenBSD system that will act as a network router that takes advantage of the OpenBSD's PF packet filter.
1. OpenBSD Installation
Install OpenBSD by using this tutorial.
Now that you have OpenBSD installed, lets proceed with the next step.
2. OpenBSD Network Configuration
The network interface is configured at boot time using the /etc/hostname.if files, where if will be replaced by the full name of your interface, for the example above, /etc/hostname.xl0.
The layout of this file is simple:
address_family address netmask broadcast [other options]
 Print This Post
Print This Post
OpenBSD: How To Install OpenBSD – OpenBSD 4.7 Installation Guide
OpenBSD is a Unix-like operating system descended from Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), a Unix derivative developed at the University of California, Berkeley.
The OpenBSD project produces a FREE, multi-platform 4.4BSD-based UNIX-like operating system. OpenBSD supports binary emulation of most programs from SVR4 (Solaris), FreeBSD, Linux, BSD/OS, SunOS and HP-UX.
This article is a step-by-step guide about how to install OpenBSD 4.7 using the installation CD. The installation guide will show a clean install, meaning any operating system or information already on the computer will be erased.
 Print This Post
Print This Post
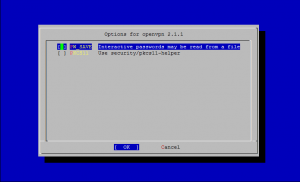
How To Install OpenVPN in FreeBSD
OpenVPN is a an open source software application that implements virtual private network (VPN) solutions for creating secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections in routed or bridged configurations and remote access facilities. OpenVPN uses SSL/TLS security for encryption and is capable of traversing network address translators and firewalls.
I. OpenVPN Server - Installation and Configuration
1. Installing OpenVPN Server
To install OpenVPN from FreeBSD ports, enter:
cd /usr/ports/security/openvpn make install clean
 Print This Post
Print This Post
Installing PowerDNS with MySQL backend and PowerAdmin On CentOS
PowerDNS is a MySQL-based DNS server, written in C++ and licensed under the GPL. PowerDNS can be managed through a web interface (PowerAdmin). This guide shows how to install it on CentOS 5.
1. Installing MySQL
# yum -y install mysql mysql-server
2. Enable MySQL on boot and start MySQL server
# chkconfig --levels 235 mysqld on
# service mysqld start
Make sure the MySQL server is running:
# netstat -tap | grep mysql
tcp 0 0 *:mysql *:* LISTEN 28179/mysqld
3. Set password for user root
# mysqladmin -u root password your_password
 Print This Post
Print This Post
How To Set Up a FTP server with ProFTPD in Ubuntu
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a network protocol used to exchange and manipulate files over a TCP/IP-based network. FTP is built on a client-server architecture and utilizes separate control and data connections between the client and server applications.
ProFTPD is a high-performance and scalable FTP server written from scratch, with a focus toward simplicity, security, and ease of configuration.
ProFTPD Features:
- Single main configuration file, with directives and directive groups
- Per directory “.ftpaccess” configuration similar to Apache's ".htaccess".
- Easy to configure multiple virtual FTP servers and anonymous FTP services.
- Anonymous FTP root directories do not require any specific directory structure, system binaries or other system files.
- Designed to run either as a stand-alone server or from inetd/xinetd, depending on system load.
- No SITE EXEC command. In modern Internet environments, such commands are a security nightmare. ProFTPD does not execute any external programs at any time. The source is available (and must always be available) for administrators to audit.
- Hidden directories and files, based on Unix-style permissions or user/group ownership.
- Runs as a configurable non-privileged user in stand-alone mode in order to decrease chances of attacks which might exploit its "root" abilities
- Logging and utmp/wtmp support with extended logging available.
- Shadow password suite support, including support for expired accounts.
- Modular design, allowing server to be extended easily with modules. Modules have been written for SQL databases, SSL/TLS encryption, LDAP servers, RADIUS support, etc.
- IPv6 support.
 Print This Post
Print This Post
FreeBSD: How To Install FreeBSD – FreeBSD 8 Installation Guide
This article is a guide to install FreeBSD 8 using an installation CD/DVD, please make sure you've got a FreeBSD 8 installation CD/DVD.
1.Starting the FreeBSD installation
Start the installation by booting up using the installation disc.
Press ENTER, the system will start hardware probe process and you will see lots of text messages flying by your screen.
Once the installer has booted up it'll ask you to select the country, system console keymap and the type of installation you want to run. You can use the UP/DOWN arrow key to select and ENTER to continue.
 Print This Post
Print This Post
MySQL Server Installation in FreeBSD using ports
This guide describes how to install MySQL, a very popular relational database, in FreeBSD.
Please make sure the ports collection is up to date. If not, run the following command:
# portsnap fetch update
Then navigate to the ports folder for MySQL:
# cd /usr/ports/databases/mysql51-server
and run:
# make install clean
This command will download required files from the internet and will install MySQL server.
Once the install is finished, we install the database
# mysql_install_db --user=mysql
and we set up the directory permissions
# chown -R mysql /var/db/mysql/
# chgrp -R mysql /var/db/mysql/
Make sure MySQL server start automatically whenever FreeBSD comes up after reboot.
FreeBSD provide this facility via system configuration information. This file lists which services should be started up at system initial boot time.
The file contains the global system configuration information referenced by the start up scripts and is stored in /etc/rc.conf.
Configure FreeBSD to start MySQL at start up
Open /etc/rc.conf file using a text editor ( I use vi but you can use your preferred editor )
# vi /etc/rc.conf
and append following line which will enable MySQL server automatically after each reboot:
mysql_enable="YES"
Save file and exit to shell prompt.
Starting MySQL server
To Start MySQL server under FreeBSD type following command (use script):
# /usr/local/etc/rc.d/mysql-server.sh start
Note: This will work only if you have mysql_enable="YES" in rc.conf. If you don't, use the following command:
# /usr/local/etc/rc.d/mysql-server.sh forcestart
MySQL Password
By default, MySQL super user account has no password. So it’s important to assign the administrator account password. To change the root password, enter the following command:
mysqladmin -u root password newpass
Replace newpass with your own desired password.
Optionally, copy either my-huge.cnf, my-large.cnf, my-medim.cnf or my-small.cnf (depending on the usage and utilization of your MySQL server) as my.cnf to /etc/ or /var/db/mysql which will enable you to tweak and change the configuration of server-specific MySQL server options by editing the file.
 Print This Post
Print This Post